How much value does your organization get from its data? To get the most benefit from your data—and to use data from a variety of sources—you need to implement a modern data stack. With a modern data stack, you’ll be able to gather data from a larger number of sources, provide faster and easier access to that data, and gain detailed insights from the data you collect.
Putting together a modern data stack requires assembling a variety of interrelated technologies and properly integrating them toward a single goal. This definitive guide to the modern data stack will help you achieve that goal.
Key Takeaways
- A modern data stack is a set of technologies designed to ingest, store, transform, and analyze data from a variety of sources.
- Modern data stacks can ingest both structured and unstructured data in a variety of formats.
- Modern data stacks typically store data in the cloud for centralized access.
- Modern data stacks include robust data quality monitoring capabilities to ensure the highest quality data possible.
What is a Data Stack?
The modern world revolves around data. According to Statista, the amount of data created, consumed, and stored will exceed 120 zettabytes this year and grow to more than 181 zettabytes by 2025. (A zettabyte is equal to 1 billion terabytes or 1 trillion gigabytes.)
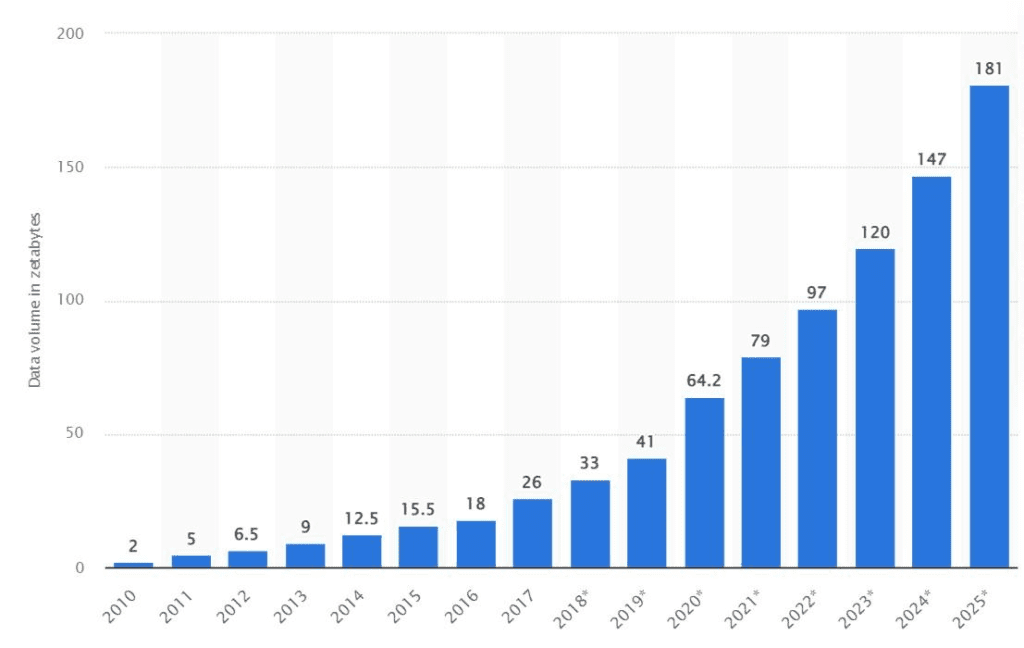
Unfortunately, most of that data is not put to good use. By some estimates, up to 60% of data in the average company goes unanalyzed. That’s a terrible waste of what should be useful data.
To make better use of this data requires a set of technologies called a data stack. A data stack gathers, transforms, and uses available data to help an organization make better operational and strategic decisions.
Modern data stacks use state-of-the-art tools to make sense of all the disparate data generated by the many different sources of data available today. These stacks utilize cloud storage and cutting-edge tools to transform and analyze both structured and unstructured data in real time. This allows companies to get immediate value from their data while ensuring the data is of high-enough quality to be useful.
What Are the Components of a Modern Data Stack?
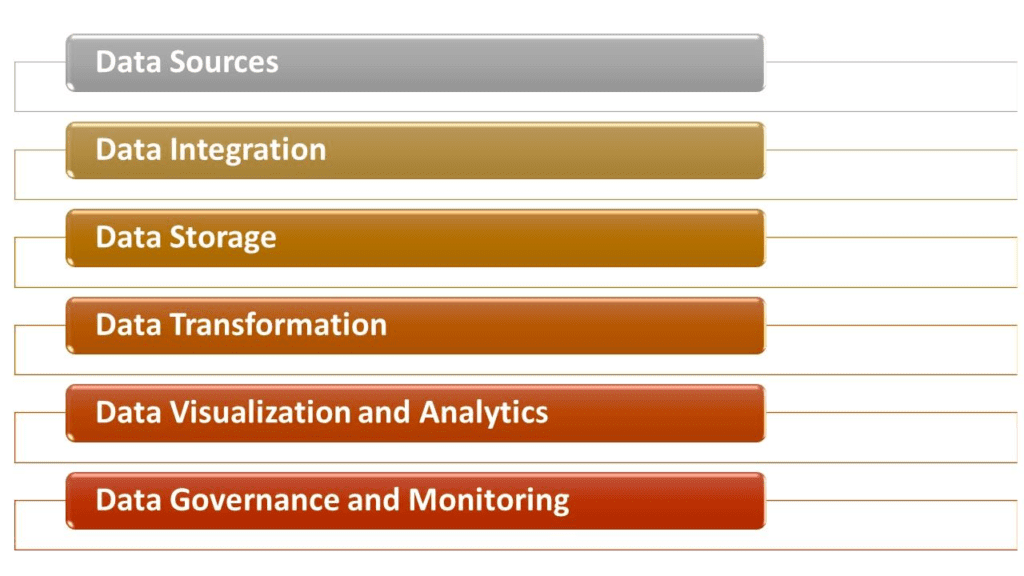
Today’s modern data stack consists of six distinct components:
- Data sources, both internal and external
- Data integration, which ingests data from different sources
- Data storage, typically in the cloud
- Data transformation, which makes data from all those sources equally accessible and usable
- Data visualization and analytics, which generates actionable insights from the transformed data
- Data governance and monitoring, which keeps track of the entire data stack and all data within
Data Sources
A modern data stack turns raw data into usable data, which means the entire process starts with raw data. Organizations typically have data coming from various sources, including:
- Internal customer and sales databases
- CRM platforms, such as Salesforce and HubSpot
- Social media, such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn
- Event streams, from website clicks and other real-time activities
- APIs, from software and apps
A modern data stack has to be able to ingest data from all these sources in near-real-time.
Data Integration
The next part of a modern data stack is data integration. This entails extracting data from its original sources, organizing, and monitoring its quality to prepare it for storage in a centralized location.
In a traditional data stack, data must first be transformed before it can be stored. This is accomplished through a process known as Extract, Transform, Load, or ETL. In a modern data stack, data does not need to be transformed before it is stored, as the transformation happens later in the process.
Instead, raw data is typically stored in its original form as part of the Extract, Load, Transform (ELT) process. Unlike the ETL process, which is typically a batch process, ELT can be done in real time as the data is streamed into the stack.
Data Storage
Ingested data must be stored somewhere. In a modern data stack, that storage is typically somewhere in the cloud. Cloud-based storage is preferred because it is centralized yet easily accessible from other locations, via the Internet. Cloud storage is also easier to maintain, more cost-effective, and easier to scale than traditional on-premises storage.
Cloud data storage can take many forms, including:
- Data warehouse
- Data lake
- Data mesh
Which architecture you choose depends on your organization’s specific needs and the types of data you typically use.
Data Transformation
In a typical modern data stack using ELT methodology, data is stored in its original format and not transformed until it is ready to be accessed and used. This enables the use of data in various formats, including both structured and unstructured data. It is transformed within the storage medium into whatever format is required for consumption.
The transformation process is also where data quality comes into play. For data to be useful it must be accurate, complete, consistent, timely, unique, and valid. Poor-quality data must be identified, separated from higher-quality data, and either cleaned or deleted. This requires data transformation tools that include robust data quality monitoring capabilities.
Data Visualization and Analytics
Once data is transformed, it can be consumed by users within the organization. This requires visualizing the data, in the form of reports and dashboards, as well as analyzing the data. Today’s modern business intelligence (BI) and analysis tools let users slice and dice the data in myriad combinations, as well as combine data from different sources to identify current and future trends. Detailed analysis, when performed on the right data, results in actionable insights that help drive business decisions.
Data Governance and Monitoring
The final component in the modern data stack is one that resides apart from the normal data flow. To keep track of the data in the stack and ensure that the process is working efficiently requires constant monitoring and governance. You need to know where your data is at all times, the state of that data, and how discoverable it is, otherwise the data you gather could become unusable and ultimately unused. Data governance is also necessary for testing and monitoring the data flow, monitoring data quality, generating detailed audit trails, and ensuring compliance with privacy and security regulations.
What Are the Benefits of a Modern Data Stack?
There are several key advantages to moving from a traditional to a modern data stack, including:
- Faster data processing and analysis speeds
- More detailed analytics
- More robust data tracking and auditing
- Ability to ingest data from disparate sources
- More automated processes
- Higher quality data
- Lower costs
In short, a modern data stack helps your organization get more use out of more different types of data than possible before. It’s an essential way to remain competitive in today’s ultra-competitive data-driven environment.
Ensure a High-Quality Modern Data Stack with First Eigen’s DataBuck
Even the most modern data stack can be rendered useless if it is fed poor-quality data. First Eigen’s DataBuck is a data quality monitoring solution that works with your data stack to automatically identify low-quality data and turn it into usable data. DataBuck’s artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities improve data processing speed, minimize errors, and reduce costs—all with minimal manual interaction.
Contact FirstEigen today to learn more about data quality in the modern data stack.
Check out these articles on Data Trustability, Observability, and Data Quality.
