Seth Rao
CEO at FirstEigen
How to Build a Data Stack That Ensures Data Quality
How does your organization manage the volumes of data ingested each day? The most effective way to ingest and manage large amounts of data is with a modern data stack. To build a data stack that meets your business needs, follow the five essential steps to ensuring the highest quality, most useable data possible outlined in this article.
Key Takeaways
- A data stack is a set of tools and technologies used to collect and transform large volumes of data.
- There are five primary components of a modern data stack: data sources, data ingestion, data warehousing, data transformation, and data analysis.
- To build an effective data stack, you need to identify your data sources, establish a data warehouse, choose data ingestion tools, determine a data modeling process, and provide robust reporting and analytics.
What is a Data Stack?
Companies today deal with massive amounts of data. Experts at the University of Tennessee note that 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are created every day – and this number is expected to increase to 44 zettabytes per day by 2025. Unfortunately, most of this data is wasted or underutilized. (A study by Seagate estimated that 68% of enterprise data goes unused.)
To manage and make better use of all this data, many companies utilize a set of tools collectively referred to as a data stack. Put simply, a data stack is a collection of technologies that collect and transform data for use within an organization.
A modern data stack must be able to ingest data from a variety of both internal and external sources, transform that data into a usable format, and provide users with the tools to extract and analyze that data. An effective cloud data stack provides the usable data that companies need to make both day-to-day operating decisions and longer-term strategic plans.
When implemented properly, a data stack not only makes large volumes of data manageable but also democratizes the use of that data. By making data more accessible to more users, a fully functional data stack improves a company’s operational and analytical capabilities.
Understanding the Components of a Data Stack
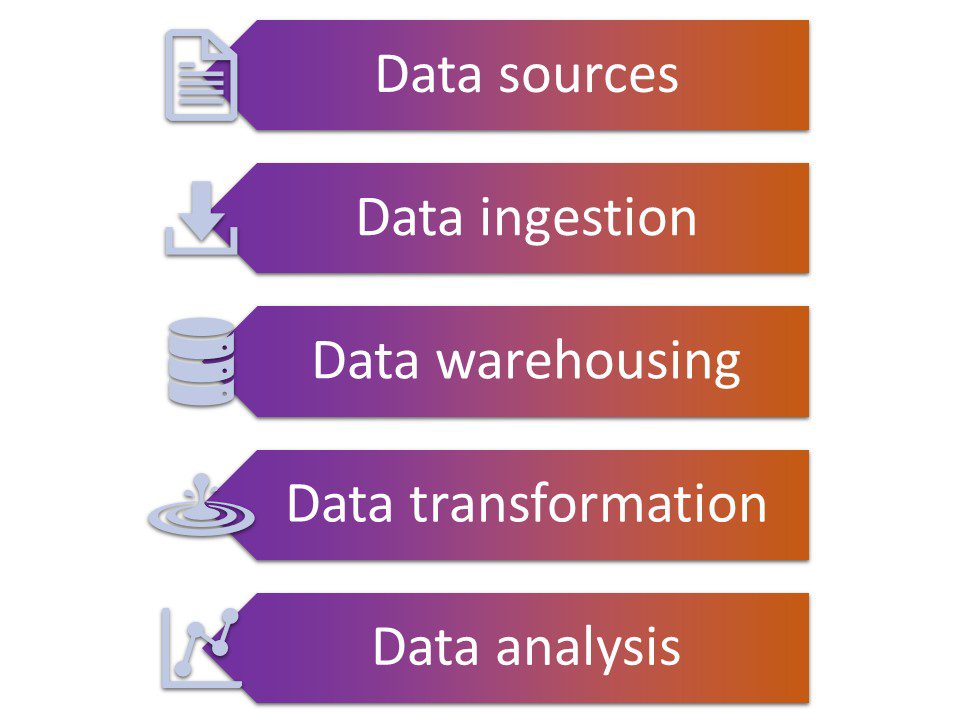
A modern data stack has five main components:
- Data sources. Most data stacks incorporate data from multiple sources. These sources can be both internal and external, including customer databases, acquired data, social media, and various event streams.
- Data ingestion. This part of the data stack ingests the data from the multiple sources.
- Data warehousing. The data warehouse stores the ingested data. Most modern data stacks use cloud-based data warehouses, although they can also be based on-premises on a network server.
- Data transformation. This part of the stack transforms the raw data into a more usable format. Data transformation typically includes data quality monitoring and cleaning.
- Data analytics. The final component of the data stack enables users to analyze the data, run reports, and obtain actionable insights.
How to Build a Data Stack in 5 Easy Steps?
How can your company build a data stack that works for your specific needs? While every situation is unique, there are five basic steps any company, regardless of type or size, can follow to build an effective and efficient data stack.
Step #1: Identify Your Data Sources
The first step in building a data stack is to identify your data sources. You need to know where your data comes from before you can determine how to store and manage it.
Depending on your organization, you may source data from:
- Office applications, such as Microsoft Word and Excel
- Customer relationship management (CRM) applications, such as Salesforce
- Internal company databases
- External databases
- Social media
- Internet of things (IoT) devices
For each of these sources, you need to consider various characteristics of the data, such as type of data, freshness, accuracy, and format. These criteria determine how the data needs to be ingested, stored, and transformed.
Step #2: Establish a Data Warehouse
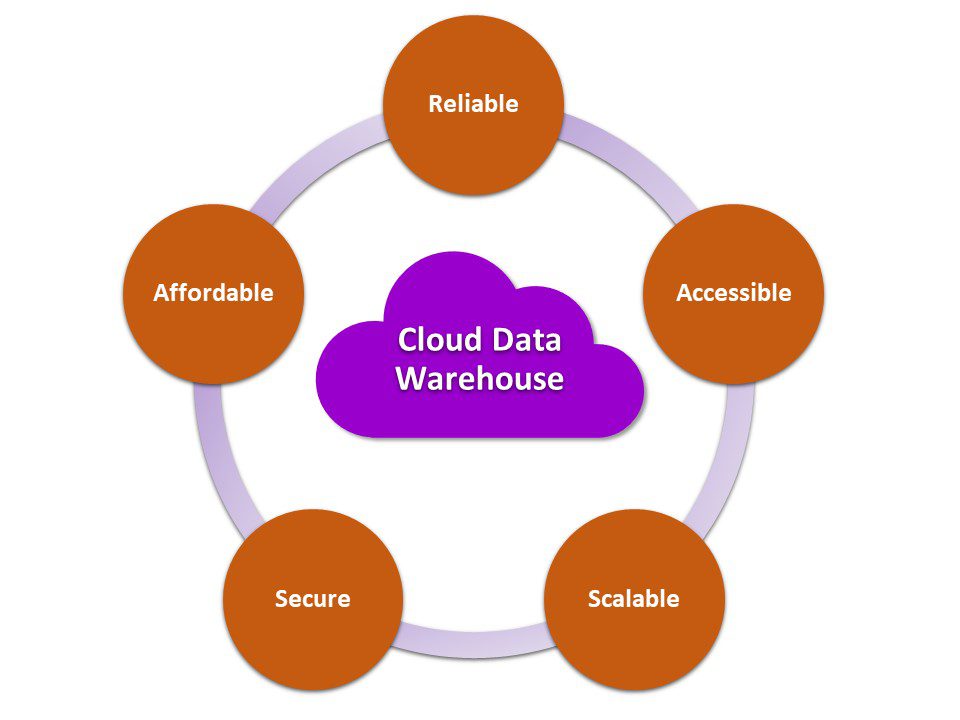
The next step in building a data stack is figuring out where and how you’ll store the ingested data. For most larger organizations, the logical choice is a data warehouse that can handle large volumes of data.
You also need to determine what type of data warehouse to establish. You can build a data warehouse on-premises, utilizing your existing network servers, or you can base it in the cloud. Cloud data warehouses have several inherent advantages over on-premises warehouses:
- Reliability: Most cloud-based data warehouses are easier to maintain and have higher uptime than traditional server solutions.
- Accessibility: Any authorized user with an Internet connection can access data stored in the cloud, making cloud-based solutions ideal for today’s growing remote workforce.
- Scalability: Expanding an on-premises data warehouse means investing in new servers and physical infrastructure. Conversely, expanding a cloud-based solution requires only the purchase of more storage space in the cloud. This means a cloud-based data warehouse can easily scale as your business and data processing needs grow.
- Security: Cloud-based data warehouse solutions have robust security measures to protect against data breaches, ransomware, and other cyberattacks.
- Affordability: Because you don’t have to invest in expensive physical infrastructure, cloud-based data warehouses have lower up-front costs as well as lower ongoing maintenance expenses.
Whichever type of data warehouse you choose, make sure it can handle your current and expected data volume, is easily manageable, and is secure against cyber threats.
Step #3: Choose Your Data Ingestion Tools
Next, you need to determine what tool(s) you’ll use to ingest data from your chosen sources into your data warehouse. Your choice of data ingestion tools should reflect the types of data you’ll be ingesting, as well as how those tools integrate with your chosen data warehouse. Look for tools that:
- Can ingest both batched and streamed data.
- Can handle various types of data, including unstructured data.
- Prioritize important data.
- Eliminate duplicates from redundant data streams.
- Offer fast and efficient ingestion.
- Have low maintenance needs and costs.
- Can work automatically with minimal human intervention.
Step #4: Determine a Data Modeling Process
Data modeling is part of the data transformation process. Data modeling tools transform raw data into usable formats while monitoring data quality and managing poor-quality data. To choose the right data modeling process, you need to consider how you plan to store your data, what data formats are acceptable, and how that data will be accessed and used.
Step #5: Provide Robust Data Analysis
The final step in building a modern data stack is designing a robust data analysis process. This step should be driven by the data’s users – data analysts as well as everyday business users. You need to know what insights users expect from the data and how they can best extract that information. This typically means creating a mix of reports and real-time dashboards to help users visualize and dig deeper into the data you manage. Look for analytics tools that are:
- Easy to use
- Customizable
- Adaptable for both casual and advanced users
- Scalable
- Capable of real-time reporting and analysis
- Produce easily sharable results
By following these steps, you can create a data stack that meets your organization’s current needs and can evolve as your needs change in the future.
Future Trends in Data Stacks
As the digital landscape evolves, data stacks must adapt to meet new demands and technologies. Here are key trends shaping the future of modern data stacks:
- Emerging Technologies:
- Serverless Architecture: Reduces infrastructure management, enabling teams to focus on development.
- Data Mesh: Decentralizes data ownership for better scalability and autonomy.
- Edge Computing: Processes data closer to the source, enhancing real-time analytics.
- Integration with AI/ML:
- Automated Data Quality: AI tools identify anomalies, ensuring real-time data accuracy.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning forecasts trends to inform decisions.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Simplifies data queries through conversational interfaces.
- Scalability and Flexibility:
- Cloud-Native Solutions: Enable dynamic scaling based on demand.
- Modular Architecture: Supports easy integration of new tools as needs evolve.
- Multi-Cloud Strategies: Optimize costs and mitigate risks by distributing data across cloud providers.
Improve the Quality of Your Data Stack with First Eigen’s DataBuck
First Eigen’s DataBuck uses the latest technologies, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, to ensure that the data flowing into and stored within your data stack is the highest possible quality. DataBuck not only automates data quality monitoring, but it also helps reduce errors, increase processing speed, and reduce costs.
Contact FirstEigen today to learn more about data quality and data stacks.
Check out these articles on Data Trustability, Observability & Data Quality Management-
FAQs
A cloud data stack offers several advantages over on-premises solutions, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, ease of maintenance, and accessibility. Cloud data stacks can be easily expanded as data volumes grow, often have lower upfront costs, and allow remote access for users, making them ideal for modern, flexible business environments.
FirstEigen’s DataBuck enhances data quality through automated monitoring, reducing errors, and increasing processing speed. It integrates seamlessly with your existing data stack, ensuring data accuracy and reliability. Additionally, DataBuck helps lower operational costs by minimizing manual intervention and optimizing data validation processes.
To future-proof your data stack, focus on scalability, flexibility, and integration with emerging technologies like AI and machine learning. Choose solutions that can easily adapt to growing data volumes and evolving business needs. Regularly review and update your stack components to incorporate the latest advancements and best practices.
Common challenges include data integration issues, ensuring data quality, and managing scalability. Address these challenges by selecting robust integration tools, implementing rigorous data quality checks, and opting for scalable cloud-based solutions. Regularly monitor and adjust your stack to keep up with changing data requirements and business goals.
Discover How Fortune 500 Companies Use DataBuck to Cut Data Validation Costs by 50%
Recent Posts
Get Started!